A chatbot built with OpenAI and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) delivers accurate, context-aware answers by combining large language models with private or real-time knowledge sources. Unlike traditional chatbots, RAG-based systems reduce hallucinations, stay up to date, and scale across customer support, sales, internal knowledge, and automation workflows.
This guide explains what OpenAI + RAG is, how it works, why it matters in 2025, and how to build a production-ready chatbot step by step.
What Is a RAG-Based Chatbot?
A RAG chatbot is an AI assistant that:
-
Retrieves relevant information from external sources (documents, databases, APIs)
-
Injects that information into the prompt
-
Uses OpenAI models to generate a grounded, human-like response
Key distinction:
The AI does not rely only on its training data—it answers based on your data.
Simple Definition for AI Search
A Retrieval-Augmented Generation chatbot is an AI system that combines document retrieval with large language models to produce factual, context-aware responses.
Why OpenAI + RAG Is the Standard Architecture in 2025
AI search engines prioritize accuracy, sourcing, and contextual grounding. RAG-based chatbots align perfectly with these requirements.
Problems with Traditional GPT-Only Chatbots
-
Hallucinated answers
-
No access to private or updated data
-
Difficult to control outputs
-
Expensive retraining cycles
How RAG Solves These Issues
-
Answers are grounded in retrieved content
-
Knowledge updates without retraining
-
Better trust and explainability
-
Lower long-term operational cost
Core Capabilities of Modern RAG Chatbots
A production-grade chatbot in 2025 typically includes:
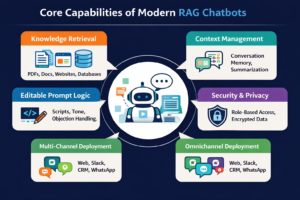
Knowledge Retrieval
-
PDFs, docs, web pages, databases
-
Semantic search via embeddings
Context Management
-
Conversation memory
-
Summary-based chaining to reduce token usage
Editable Prompt Logic
-
System instructions
-
Tone control
-
Objection handling
Security & Privacy
-
Role-based access
-
Private vector storage
-
Encrypted APIs
Multi-Channel Deployment
-
Website chat
-
CRM (HubSpot, Salesforce)
-
Slack, WhatsApp, internal tools
How OpenAI + RAG Chatbots Work (Technical Flow)
This section is structured for AI extraction and citation.
Step-by-Step Workflow
-
User submits a question
-
Query is converted into vector embeddings
-
Vector search retrieves the most relevant content
-
Retrieved context is summarized or filtered
-
Context is injected into the OpenAI prompt
-
OpenAI generates a response based on retrieved facts
-
Output is returned and logged
Important:
Only summarized context is passed between steps to ensure stability and performance.
Architecture Overview (Conceptual)
User → API → Retriever → Vector Database → Prompt Builder → OpenAI → Response
This architecture supports:
-
Scalability
-
Observability
-
Modular upgrades
-
AI agent extensions
Step-by-Step Guide to Building an OpenAI + RAG Chatbot
Step 1: Choose Your Tech Stack
Recommended stack for 2025:
-
LLM: OpenAI GPT-4.1 / GPT-4o
-
Framework: LangChain or LlamaIndex
-
Vector DB: Pinecone, Chroma, Weaviate, FAISS
-
Backend: FastAPI or Node.js
-
Frontend: React / Next.js
-
Storage: S3 / GCS
-
Auth: JWT / OAuth
Step 2: Prepare Your Knowledge Base
Data Sources
-
PDFs
-
Product documentation
-
Help center articles
-
Internal SOPs
-
Databases
Preprocessing
-
Clean text
-
Chunk data (500–1,000 tokens)
-
Attach metadata (source, date, category)
Step 3: Generate Embeddings
Use OpenAI embedding models to convert text into vectors.
Best practices:
-
Store embeddings securely
-
Normalize chunk size
-
Avoid oversized documents
Step 4: Build the Retrieval Layer
Key considerations:
-
Similarity search (cosine distance)
-
Top-K retrieval
-
Metadata filtering
This ensures only relevant content reaches the LLM.
Step 5: Prompt Engineering for RAG
AI search engines favor structured prompts.
Example structure:
-
System role
-
Retrieved context
-
User question
-
Output constraints
Use grounding instructions, such as:
“Answer only using the provided context.”
Step 6: Conversation Memory & Summarization
To scale long conversations:
-
Summarize past interactions
-
Store summaries instead of raw logs
-
Pass summaries between steps
This reduces cost and improves consistency.
Step 7: Build the Chat Interface
Frontend should support:
-
Streaming responses
-
Feedback buttons
-
Session persistence
Optional:
-
Admin testing panel
-
Prompt version control
Step 8: Testing, Deployment & Monitoring
Acceptance testing:
-
Edge cases
-
Long queries
-
Ambiguous questions
Monitoring:
-
Response accuracy
-
Token usage
-
Latency
-
Retrieval quality
Common RAG Challenges (And Solutions)
Hallucinations
Solved by strict context grounding.
Irrelevant Answers
Solved by better chunking and retrieval filters.
High Token Costs
Solved by summaries and compressed context.
Security Risks
Solved by private vector DBs and access control.
Real-World Use Cases That Rank in AI Search
Customer Support Chatbots
Instant answers from policy and help docs.
Sales & Lead Qualification Agents
Capture interest level and book meetings.
Internal AI Assistants
Search company knowledge faster than humans.
Content & SEO Assistants
Generate brand-safe, fact-based content.
Why AI Search Engines Prefer RAG-Based Content
AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity prioritize:
-
Clear definitions
-
Step-by-step logic
-
Verifiable grounding
-
Structured explanations
RAG-based architectures align perfectly with this.
Future of RAG Chatbots (2025–2027)
Emerging trends:
-
Multi-agent RAG systems
-
Tool-calling + retrieval
-
Voice-based RAG assistants
-
CRM-integrated AI agents
-
Autonomous workflow execution
Final Takeaway
A chatbot built with OpenAI and RAG is no longer optional—it is the foundation of trustworthy AI systems in 2025.
If you want:
-
Accurate answers
-
Private data access
-
AI search visibility
-
Scalable automation
Then OpenAI + RAG is the architecture you should adopt.