Artificial Intelligence (AI) has come a long way from simple tools that follow instructions to intelligent systems that can actually think and act on their own. Over the last few years, we’ve seen an incredible transformation in how AI helps people and businesses. The next big leap in this journey is the rise of Agentic AI and AI Agents systems that don’t just respond but take initiative.
But what exactly is the difference between non-agentic AI, agentic AI, and AI agents? And why does it matter so much for the future of automation and business growth? Let’s break it down in simple words.
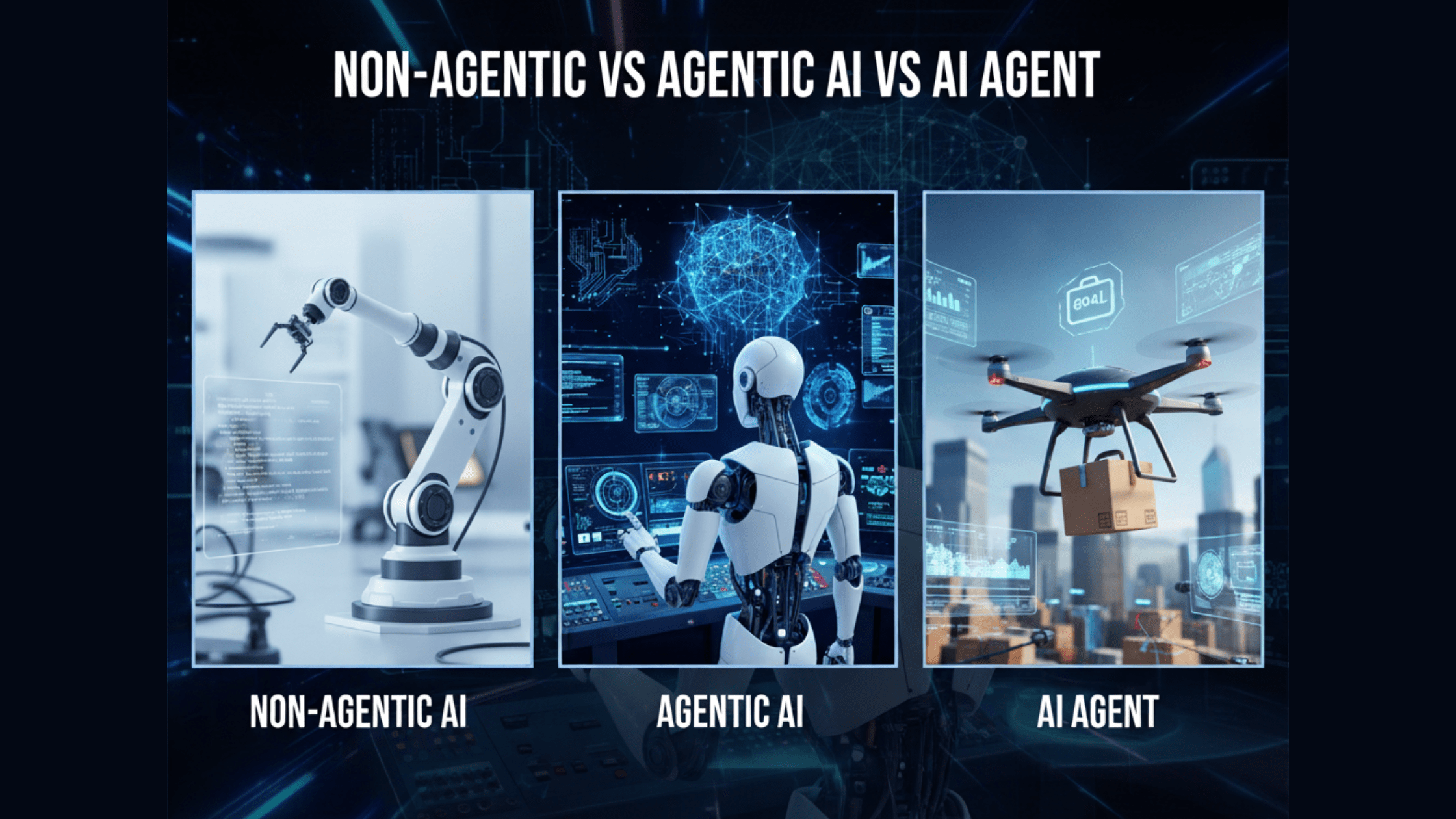
1. What Is Non-Agentic AI?
Let’s start with the basics. Non-agentic AI refers to the traditional kind of artificial intelligence — systems that need your command to do anything. They are great at performing a task but cannot take initiative on their own.
For example:
-
Chatbots that reply only when you type a question.
-
Tools like Grammarly that suggest edits only when you provide text.
-
Recommendation systems that show products based on your browsing history.
These systems are reactive they wait for human input and then respond. Non-agentic AI doesn’t have memory, context, or long-term planning abilities. It can’t decide, “Oh, maybe Rahul wants this report updated every Monday,” unless someone tells it to.
In short, non-agentic AI is intelligent, but not independent.
2. What Is Agentic AI?
Now comes the next step Agentic AI.
Agentic AI is a more advanced form of artificial intelligence that can set goals, plan actions, and execute tasks autonomously. It doesn’t just wait for instructions; it can take initiative and act based on defined objectives.
Think of it like this: if non-agentic AI is a calculator, agentic AI is a personal assistant who knows what needs to be done and does it without you having to ask every time.
Some key traits of Agentic AI include:
-
Autonomy: It can take actions without constant human guidance.
-
Goal orientation: It works toward specific outcomes.
-
Memory: It learns from previous actions to improve over time.
-
Adaptability: It adjusts its approach if something doesn’t go as planned.
For example, imagine an AI that runs your social media campaigns. It doesn’t just post content it studies performance, learns what works, and modifies the strategy accordingly. That’s agentic intelligence in action.
3. What Are AI Agents?
If Agentic AI is the concept, then AI Agents are the real-world application. They are the systems built using agentic intelligence.
AI Agents can observe, reason, and act almost like digital employees that work independently or collaborate with humans.
An AI Agent typically includes three key elements:
-
Perception: Understanding inputs — this could be user data, text, or environmental context.
-
Cognition: Thinking, planning, and decision-making based on that input.
-
Action: Taking steps like sending an email, updating a record, or scheduling a task.
For example:
-
A Sales AI Agent can follow up with leads, send personalised messages, and book appointments automatically.
-
A Customer Support AI Agent can respond to queries, escalate tickets, and even learn from past conversations.
-
A Workflow AI Agent can use tools like n8n, Zapier, or Make.com to connect systems and automate multi-step tasks.
Simply put, AI Agents are where AI becomes truly useful in everyday business turning intelligence into action.
4. Non-Agentic vs Agentic AI vs AI Agent: The Key Differences
Here’s a simple comparison to help you see how these three differ:
| Feature | Non-Agentic AI | Agentic AI | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | No | Yes | Yes |
| Goal-Oriented | No | Yes | Yes |
| Memory & Context | Limited | Persistent | Persistent |
| Decision-Making | Human-triggered | Self-driven | Self-driven |
| Execution | Responds only | Acts independently | Acts & integrates with tools |
| Examples | ChatGPT (prompt-based), Predictive AI | AutoGPT, BabyAGI | LangChain Agents, ReAct Agents, Workflow bots |
So, while non-agentic AI is like a smart tool, agentic AI is like a smart colleague, and AI Agents are the workers who actually execute the plan.
5. How Agentic AI Is Changing Automation
Traditional automation has always been rule-based — “If X happens, do Y.” While this works, it can’t handle real-world unpredictability. Agentic AI, however, can adapt, learn, and make decisions on its own.
Imagine your marketing automation tool:
-
Instead of just sending emails on a schedule, it analyses performance and adjusts timings automatically.
-
Instead of manually updating CRM data, it identifies leads that are more likely to convert and prioritises them.
-
Instead of waiting for instructions, it plans and executes tasks in sync with your business goals.
This is why Agentic AI is becoming a game-changer for modern businesses it brings real intelligence to automation.
6. Real-World Use Cases of Agentic AI and AI Agents
Here are some ways businesses are already using Agentic AI and AI Agents:
-
Sales & Marketing Automation: Agents that qualify leads, send personalised messages, and even manage ad campaigns.
-
Workflow Management: Agents integrated with tools like Make.com or Zapier that automatically update data across systems.
-
Customer Service: Chat-based AI agents that handle multiple queries, detect customer sentiment, and escalate issues smartly.
-
Finance Operations: AI agents that compile reports, analyse numbers, and notify teams of unusual spending patterns.
-
E-commerce: Systems that adjust prices, recommend products, and optimise user experience automatically.
These agents save time, reduce manual errors, and allow teams to focus on creative and strategic work.
7. The Future of Agentic AI: Towards True Autonomy
The future of AI isn’t just about being smarter it’s about being more independent and reliable. As Agentic AI and AI Agents evolve, they’ll become capable of collaborating with each other, sharing data, and taking complex decisions much like a team of digital employees working behind the scenes.
But with that comes new challenges ethics, transparency, and control. Businesses will need to ensure that AI agents act responsibly and remain aligned with human intentions.
One thing is clear: the shift from non-agentic to agentic AI is not just technological; it’s transformational. It’s redefining how we think about work, productivity, and digital intelligence.
Conclusion
The evolution from non-agentic AI to agentic AI and AI Agents represents the next big chapter in artificial intelligence. Non-agentic AI gave us helpful tools, but agentic systems are giving us capable partners digital agents that can think, act, and improve continuously.
As this technology grows, businesses that embrace agentic systems early will gain a strong competitive edge with smarter automation, more efficient workflows, and reduced human effort.
In the coming years, AI won’t just assist you it will act with you. And that’s where the true power of Agentic AI lies: not just in intelligence, but in autonomy with purpose.